Dr Wood
Provide Feedback
CloseShare With Contacts
CloseShare With Contacts
CloseCopy Link
Closehttps://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Delete Message?
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
An update is now available for this app!
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
There are no people to display!
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?

You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?

Our Pre-Admission staff will call you the business day prior to your admission to confirm your admission time and explain any clinical preparation. If you have not received a call or will be difficult to contact, please call +61 2 9923 7115 after 2.00pm the business day prior to your admission. (See our Patient Admission Guide )
You will need to fast for your anaesthetic so please follow the instructions given to you by the Pre-Admission staff.
The customer services team will also contact you the business day prior to your admission to explain any out of pocket expenses associated with your admission. We ask that you finalise these expenses on admission. If you do not have any out of pocket expenses you will not receive a call.
Please shower before you come to Mater Orthopaedic Day Surgery, use minimal make-up and, for comfort following your procedure, wear loose clothing. Do not wear nail polish or jewellery.
Report to the Mater Orthopaedic Day Surgery Unit in the Mater Clinic (see FAQ). Access is from the lifts of the Mater Clinic car park or via the Mater Hospital.
Do not bring cash, jewellery or valuables of any kind as the Mater Clinic cannot be responsible for any valuables or missing items.
When discharged please visit the orthopaedic day surgery reception to settle your account. We accept payment by cash, EFTPOS (check your daily limit), Visa, MasterCard, Amex and cheque, but not Diners Club. Following health fund payment of your claim, any balance owing will be debited to your credit card.
Please make sure you return your paperwork to the Mater Hospital prior your admission - fax, mail or drop off.
The day before procedure you will receive a phone call from one of the nursing staff with your admission time.
During this phone call please advise the nurse of any medications you are currently on and they will let you know which ones to continue and which to cease.
Always cease anti-inflammatory medications 24 hours prior surgery.
Please notify the day surgery asap if you have any blemishes to the operative site (eg cuts, grazes, pimples). You may be required to take a photo and sned it to us so we can review it. We want to make sure your procedure is as safe as possible.
You must be fasted (ie NO food, liquid - including water, gum, lollies etc) for a minimum of 6 hours prior your procedure.
Your procedure may be cancelled if you have not fasted prior surgery.
Once your surgery is booked, please contact the Mater Orthopeadic Surgery if you suffer from:
Parking is available within the Mater Clinic. Access to the car park is from the main hospital entrance off Rocklands Road.
A patient drop off / pick up zone is located outside the Mater Clinic. Drive in through the car park boom gate, go straight ahead, down the ramp and veer right. The first 15 minutes after entering the car park are free.
We recommend this method when picking up your loved one. Once in the Pick Up Area call the nurses +61 2 9923 7118 and we will walk/whellchair the patient directly to your car.
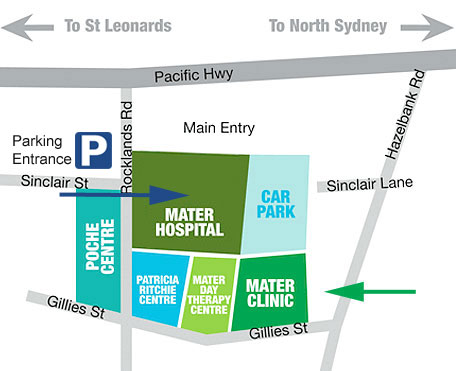
Mater Orthopaedic Surgery is a closed unit as we operate three theatres from within the unit. Therefore once you farewell your loved one at pre-op, you will be unable to to see them until they are officially discharged from recovery.
If you would like a Status Update you can ring the nurces in recovery +61 2 9923 7119
This is best done 5-6 hours after you say goodbye. As you can appreciate, we receive many calls from family members, however our main priority is the well-being of our patients, so please keep calls to a minimum.
The general turn around time for the day procedures is 6-8 hours from admission to discharge.
However, this will vary depending on the individual and their procedure. bear in mind, also, that everyone responds differently to anaesthetics and so recovery time does vary and can not be predicted. As this is day surgery, please keep the whole day free, just in case.
If you have questions pre or post procedure you can email mods@matersydney.com.au One of our nursing staff with reply within 24 hours.












A drug-induced depression of the Central Nervous System that results in a loss of response and perception to all external stimulation.
Each surgeon has a regular anaesthetist to work alongside them. You will be cared for and monitored by this anaesthetist throughout the entire procedure. They are all fully accredited anaesthetists.
Your anaesthetist will care for you by:
If you have any concerns your anaesthetist is available to be contacted before and after your surgery.
Waking up in recovery can sometimes be a bit disorientating and confusing.
However to help you prepare, you can expect:
There may be some post-operative pain.
We use the pain scale (shown below) and rate surgical pain to be around the 6 mark.
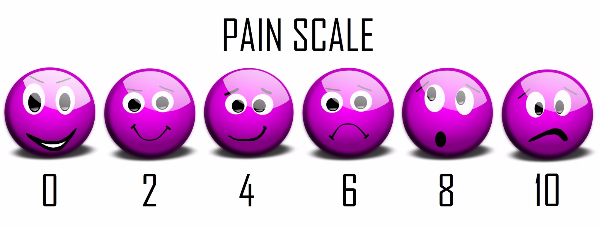
Stage 1 Waking up from the anaesthetic and pain-relief
Stage 2 Further recovery/rest
Stage 3 (final) Discharge information/instructions given
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Downloadable information for patients and healthcare professionals. Click image to view document.
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You haven’t selected any files to be shared. Tap the Share button below documents to add them to this list. Return here to send them by email.
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
The function of the anterior cruciate ligament is to control the amount of twisting which can take place between the top part of the knee (femur) and the bottom part of the knee (tibia). The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is found in the centre of the knee joint and is often injured by a sudden strong twisting motion, eg losing control of your skis or falling off a ladder.
If the ACL is ruptured and the knee twists the two parts of the knee joint clunk against each other, resulting in damage to the meniscus and/or articular cartilage. The damage may be very severe or mild but with time the damage accumulates and may lead to early arthritis.
The aim of ACL reconstruction is to improve your quality of life and to slow down the destruction of the knee joint.
Please refer to the Pre Operative Information sheet.
An arthroscope is introduced into the joint and the joint is inspected. All visible damage is corrected. The area which used to be occupied by the anterior cruciate ligament is cleared and the bone surfaces are prepared to take the new ligament. The graft is usually a double stranded hamstring, ie using semi tendonosis and gracilis tendons. In some circumstances a mid third patella tendon graft is used and the bony plugs in the femur and the tibia are fixed with screws.
When a hamstring graft is taken, a tunnel is drilled in the tibia and in the femur and the graft placed as close to its original position as possible. It is fixed in the femur by an Endobutton and in the tibia, usually by a screw, and secured with a staple.
A patient's progress after surgery is significantly altered by other problems that may be encountered in the knee at the time of surgery. If there are any cartilage defects, then persistent pain and swelling is to be expected after surgery.
Reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament involves a day in hospital. Drains are removed approximately four hours post surgery. You will commence some basic range of movement exercises. Instructions will be given on how to use crutches and you will be taken for a walk.
You will be given a description of all the exercises and it is suggested that you continue to practise them at home every hour or so.
Do Exercise as often as possible - little but often is best, eg 5 minutes each hour
Do Keep the leg elevated when not walking
Do Stay on crutches until advised otherwise
Do Apply ice to the knee if you are concerned about any swelling
Do If braced, adjust the brace as necessary as it will tend to slip as the leg loses some bulk, ie loosen the straps, adjust the hinges of the brace so they are opposite your knee cap, then tighten the velcro straps
Do Ensure the leg does not get wet until the wounds are clean and dry
Don't Drink too much alcohol, especially in the first few weeks as the leg may become swollen and walking with crutches may be difficult.
Walking for the first time using crutches can be difficult
When attempting to walk with crutches, there are a few important points to keep in mind
When going up, take your weight through your crutches and move your unaffected leg onto the first step. Take your weight through this leg and then move your crutches and injured leg up onto the same step.
When going down, take your weight through your unaffected leg and move your crutches down onto the first step. Take your weight through the crutches and move the injured leg onto the step, followed by your unaffected leg.
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
This prevention program consists of a warm-up, stretching, strengthening, plyometrics, and sport specific agilities to address potential deficits in the strength and coordination of the stabilizing muscles around the knee joint. It is important to use proper technique during all of the exercises. The coaches and trainers need to emphasize correct posture, straight up and down jumps without excessive side-to-side movement, and reinforce soft landings.
This program should be completed 3 times a week. If you are using this program with athletes that are twelve or under, please perform the plyometrics over a visual line on the field or a flat 2" cone and land each jump with two feet. Do not perform single leg plyometrics with young individuals until they demonstrate substantial control. (see addendum) The field should be set up 10 minutes prior to the warm-up. This will allow for a smooth transition between the activities. A sample field set-up has been included in your packet.
This program should take approximately 15 - 20 minutes to complete. However, when you first begin the program, it may take slightly longer due to the fact that you must first become well acquainted with the program and the transitions. Along side each exercise you will notice a box with the approximate amount of time that should be spent on each activity. This will serve as a guideline to you in order to conduct your warm-up in a time efficient manner.
Warming up and cooling down are a critical part of a training program. The purpose of the warm-up section is to allow the athlete to prepare for activity. By warming up your muscles first, you greatly reduce the risk of injury.
Elapsed Time: 0 - .5 minute
Purpose: Allows the athletes to slowly prepare themselves for the training session while minimizing the risk for injury. Educate athletes on good running technique; keep the hip/knee/ankle in straight alignment without the knee caving in or the feet whipping out to the side.
Instruction: Complete a slow jog from near to far sideline
Elapsed Time: .5 to 1 minute
Purpose: engage hip muscles (inner and outer thigh). This exercise will promote increased speed. Discourage inward caving of the knee joint.
Instruction: Start is an athletic stance with a slight bend at the knee. Leading with the right foot, sidestep pushing off with the left foot (back leg). When you drive off with the back leg, be sure the hip/knee/ankle are in a straight line. Switch sides at half field.
Elapsed Time: 1 – 1.5 minutes
Purpose: continued warm-up; engage hip extensors/hamstrings. Make sure the athlete lands on her toes. Be sure to watch for locking of the knee joint. As the athlete brings her foot back, make sure she maintains a slight bend to the knee.
Instruction: Run backwards from sideline to sideline. Land on your toes without extending the knee. Stay on your toes and keep the knees slightly bent at all times.
This portion of the program focuses on increasing leg strength. This will lead to increased leg strength and a more stable knee joint. Technique is everything; close attention must be paid to the performance of these exercises in order to avoid injury.
Elapsed Time: 1.5 – 2.5 min
Purpose: Strengthen the thigh (quadriceps) muscle.
Instruction: Lunge forward leading with your right leg. Push off with your right leg and lunge forward with your left leg. Drop the back knee straight down. Make sure that your keep your front knee over your ankle. Control the motion and try to avoid you front knee from caving inward. If you can't see your toes on your leading leg, you are doing the exercise incorrectly.
Elapsed Time: 2.5 –3.5 min
Purpose: Strengthen hamstrings muscles
Instruction: Kneel on the ground with hands at your side. Have a partner hold firmly at your ankles. With a straight back, lead forward leading with your hips. Your knee, hip and shoulder should be in a straight line as you lean toward the ground. Do not bend at the waist. You should feel the hamstrings in the back of your thigh working. Repeat the exercise for 30 seconds and switch with your partner.
Elapsed Time: 3.5 – 4.5 min
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the calf muscle and increases balance.
Instruction: Stand up with your arms at your side. Bend the left knee up and maintain your balance. Slowly rise up on your right toes with good balance. You may hold your arms out ahead of you in order to help. Slowly repeat 30 times and switch to the other side. As you get stronger, you may need to add additional repetitions to this exercise to continue the strengthening effect of the exercise.
These exercises are explosive and help to build, power, strength and speed. The most important element when considering performance technique is the landing. It must be soft! When you land from a jump, you want to softly accept your weight on the balls of your feet slowly rolling back to the heel with a bent knee and a bent hip. These exercises are basic, however, it is critical to perform them correctly. Please begin these exercise using a flat cone (2 inches) or with a visual line on the field.
Elapsed Time: 4.5 – 5min
Purpose: Increase power/strength emphasizing neuromuscular control
Instruction: Stand with a 2" cone to your left. Hop to the left over the cone softly landing on the balls of your feet land bending at the knee. Repeat this exercise hopping to the right. Progress to Single leg hops
Elapsed Time: 5 – 5.5 min
Purpose: Increase power/strength emphasizing neuromuscular control
Instruction: Hop over the cone softly landing on the balls of your feet and bending at the knee. Now, hop backwards over the ball using the same landing technique. Be careful not to snap your knee back to straighten it. You want to maintain a slight bend to the knee.
Elapsed Time: 5.5 – 6 min
Purpose: Increase power/strength emphasizing neuromuscular control.
Instruction: Hop over the cone landing on the ball of your foot bending at the knee. Now, hop backwards over the ball using the same landing technique. Be careful not to snap your knee back to straighten it. You want to maintain a slight bend to the knee. Now, stand on the left leg and repeat the exercise. Increase the number of repetitions as needed.
Elapsed Time: 6 – 6.5 min
Purpose: Increase height of vertical jump.
Instruction: Stand forward with hands at your side. Slightly bend the knees and push off jumping straight up. Remember the proper landing technique; accept the weight on the ball of your foot with a slight bend to the knee.
Elapsed Time: 6.5 – 7 min
Purpose: Increase power and strength of vertical jump.
Instruction: Lunge forward leading with your right leg. Keep your knee over your ankle. Now, push off with your right foot and propel your left leg forward into a lunge position. Be sure your knee does not cave in or out. It should be stable and directly over the ankle. Remember the proper landing technique; accept the weight on the ball of your foot with a slight bend to the knee. Repeat 20 times.
Elapsed Time: 7 – 8 min
Purpose: Increase dynamic stability of the ankle/knee/hip complex
Instruction: Starting at the first cone, sprint forward to the second cone. As you approach the cone, use a 3 step quick stop to decelerate. Continue on to cone 2 using the same strategy to deceleration. Do not let your knee extend over your toe. Do not let you knee cave inward. This exercise is used to teach the athlete how to properly accelerate and decelerate while moving forward and the hip, buttock and hamstring musculature.
Elapsed Time: 8 – 9 min
Purpose: To encourage proper technique/stabilization of the hip and knee. This exercise will also deter a “knock knee" position from occurring – which is a dangerous position for the ACL.
Instruction: Face forward and laterally run to the first cone on the right. Pivot off the right foot and shuttle run to the second cone. Now pivot off the left leg and continue onto the third cone. Make sure that the outside leg does not cave in. Keep a slight bend to the knee and hip and make sure the knee stays over the ankle joint.
Elapsed Time: 9 – 10 min
Purpose: To increase hip flexion strength/increase power/speed
Instruction: Starting on the near sideline, run to the far side with knees up toward chest. Bring your knees up high. Land on the ball of your foot with a slight bend at the knee and a straight hip. Increase the distance as this exercise gets easier.
It is important to incorporate a short warm-up prior to stretching. Never stretch a “cold muscle". By performing these stretches, you can improve and maintain your range of motion, reduce stiffness in your joints, reduce post- exercise soreness, reduce the risk of injury and improve your overall mobility and performance. Note: this portion of the program may be moved to the end of your training session. Do a warm-up such as brisk walking for five to 10 minutes before stretching. Gently stretch to a point of tension and hold. Hold the stretch for 30 seconds. Concentrate on lengthening the muscles you are stretching. Breathe normally.
Elapsed Time: 10 to 11 minutes
Purpose: stretch the calf muscle of the lower leg
Instruction: Stand leading with your right leg. Bend forward at the waist and place your hands on the ground (V formation). Keep your right knee slightly bent and your left leg straight. Make sure your left foot is flat on the ground. Do not bounce during the stretch. Hold for 30 seconds. Switch sides and repeat.
Elapsed Time: 11 to 12 minutes
Purpose: stretch the quadricep muscle of the front of the thigh
Instruction: Place your left hand on your partner's left shoulder. Reach back with your right hand and grab the front of your right ankle. Bring your heel to buttock. Make sure your knee is pointed down toward the ground. Keep your right leg close to your left. Don't allow knee to wing out to the side and do not bend at the waist. Hold for 30 seconds and switch sides
Elapsed Time: 12 – 13 min
Purpose: To stretch the hamstring muscles of the back of the thigh.
Instruction: Sit on the ground with your right leg extended out in front of you. Bend your left knee and rest the bottom of your foot on your right inner thigh. With a straight back, try to bring your chest toward your knee. Do not round your back. If you can, reach down toward your toes and pull them up toward your head. Do not bounce. Hold for 30 seconds and repeat with the other leg.
Elapsed Time: 13 – 14 min
Purpose: Elongate the muscles of the inner thigh (adductor group)
Instruction: Remain seated on the ground. Spread you legs evenly apart. Slowly lower yourself to the center with a straight back. You want to feel a stretch in the inner thigh. Now reach toward the right with the right arm. Bring your left arm overhead the stretch over to the right. Hold the stretch and repeat on the opposite side.
Elapsed Time: 14 - 15 min
Purpose: Elongate the hip flexors of the front of the thigh.
Instruction: Lunge forward leading with your right leg. Drop your left knee down to the ground. Placing your hands on top of your right thigh, lean forward with your hips. The hips should be square with your shoulders. If possible, maintain your balance and lift back for the left ankle and pull your heel to your buttocks. Hold for 30 seconds and repeat on the other side.
We all know how imperative a cool down is. Please don't skip it. It allows the muscles that have been working hard throughout the training session to elongate and deters the onset of muscle soreness. Please emphasize the importance of adequate fluid intake (optimally water). The cool down should take approximately 10 minutes. It should begin with a slow jog to allow the heart rate to come down before stretching. This should be followed by some light strength training exercises. In addition to those basic stretches, we are offering some additional stretches to target 3 muscle groups that are often forgotten.
Purpose: Strengthen outer hip muscles (Hip abductors, flexors) and buttocks
Instruction: Lie on the ground with your knees bent with feet on the ground. Raise your buttocks up off the ground and squeeze. Now, lift your right foot off the ground and make sure that your right hip does not dip down. Lower your right foot and now lift your left foot making sure your left hip does not dip down. Repeat 30 times on each side. As you get stronger, you will place your feet on top of a ball and repeat the exercise.
Purpose: Strengthen the abdominals (rectus abdominus, obliques)
Instruction: Lie on the ground with you knees bent. Place your hands behind your head with your elbows out wide. Support your neck lightly with your fingers. Take a deep breath in and slowly contract your abdominal muscles as you exhale. Repeat 30 times. Drop your legs off to the right side. Slowly crunch up with your elbows out wide. You should feel your oblique muscles working on the side of your waist. Repeat 30 times and switch to the other side.
Purpose: Elongate the low back muscles
Instruction: Lie on your back. Bring your right knee toward your chest and hug firmly. Keep your left leg out straight in front of you. You should feel a stretch along your low back and into your buttocks. Hold the stretch for 30 seconds and switch sides. Now bring both knees to chest. If you feel any pain in the low back, discontinue the stretch and inform your coach/trainer.
Purpose: Elongate the rotators of the hip.
Instruction: Lie on your back and bend both of your knees. Fold your left ankle over your right knee. Place your hands behind your right thigh and pull your right knee to chest. You should feel a good stretch in the left gluteals region and the side of the thigh. Hold for 30 seconds and repeat on the other side. If you experience and low back pain with this stretch, slowly lower your legs down and let your coach/trainer know.
Purpose: Elongate the inner thigh muscles (adductors).
Instruction: Sit up bringing your feet in so that the soles of your feet are touching. Gently place your elbows on your knees and slowly push down. You should feel a good stretch of the inner thigh. Hold this for 30 seconds and repeat 2 to 3 times.
This program is safe to use for male and female athletes over the age of 12. You can safely utilize this program with younger athletes by making the modifications described below:
With the plyometric activities, have your younger athletes jump over a visual line on the field (midfield, end line, or sideline) or a flat 2" cone. The emphasis of this activity is the landing technique – not the height of the object that the athlete is jumping over.
In addition, the younger athletes should perform the plyometric activities with a two-legged landing. Again, the emphasis is on the landing and knee control (not allowing the knees to cave inward and bending the knees and the hips to accept the force of landing).
Repetitions are not emphasized in this program – time is. We would prefer to see 5 repetitions with perfect biomechanical technique completed in the allotted time period as opposed to doing ten repetitions haphazardly.
This program should be completed at the BEGINNING of the practice session. If you attempt to use this program after your training session, your athletes will be fatigued and their biomechanical technique will suffer. The element of fatigue can put your athletes at a higher risk for injury.

You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
The knee has the following structures:
Knees are a marvelous invention and without them you could not easily kick a ball, kneel down or climb into a car. The knee's meniscus is tissue designed to absorb the shock of weight and the motion of the body. Too much stress can injure this shock absorber. However, meniscal tears can be effectively treated with surgery and rehabilitation which means you can usually return to an active lifestyle.
A meniscal tear is commonly the result of a twist – a typical injury for someone like a netballer - or from repeated squatting. These tears create uneven surfaces that irritate the joint and may cause pain, swelling and a catching sensation. They often require surgery since they may not heal on their own. If not corrected, a meniscal tear can lead to more serious problems such as arthritis.
A meniscal tear acts like dirt in the ball bearings of a machine. The longer the torn tissue is there the more irritation it causes and an early evaluation by an orthopaedic surgeon means earlier treatment and less damage to the joint. Meniscal surgery can repair or remove torn uneven cartilage and rehabilitation with a physiotherapist ensures the best chance of a rapid recovery.
Arthritis means an inflammation of a joint causing pain, swelling, stiffness, instability and often deformity. Severe arthritis interferes with activities and limits lifestyle.
Osteoarthritis or Degenerative Joint Disease is the most common type of arthritis. Osteoarthritis is also known as “wear and tear arthritis", since the cartilage wears out. When cartilage wears away, bone rubs on bone causing severe pain and disability. The most frequent reason for osteoarthritis is genetic, since the durability of each individual's cartilage is based on genetics. If your parents have arthritis you may also get it.
Trauma can also lead to osteoarthritis. A heavy fall or blow to the knee can injure the joint. If the injury does not heal properly, extra force may be placed on the joint, which over time can cause the cartilage to wear away.
When the articular cartilage wears away and is damaged it will become irregular, fissured and fall off revealing the bone. The damage is classified as mild or Grade III when it is irregular or fissured. The damage is classified as severe or Grade IV when the bone is revealed.
The articular cartilage can be damaged or wear away. If this happens the underlying bones rub together, producing the pain and inflammation typical of arthritis.
Arthroscopic surgery is used to correct mechanical problems within the knee joint. Unfortunately once the structures in the joint have become damaged failure to correct the damage will result in further deterioration of the knee.
An arthroscopy is a minimally invasive ('Key hole") operation to repair or investigate the integrity of a joint. Your surgeon examines the joint with an arthroscope (joint camera) while making repairs if needed through a small incision.
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
During exercise highly active muscles require large amounts of oxygen and glucose which require high blood flow down the arteries. This leads to “pumping up" of the muscles.
In some individuals the fascia surrounding the muscles is too tight to allow the muscle to swell during exercise. This leads to an increase in pressure inside the muscle compartment. When the pressure rises the veins become compressed because their walls are much softer.
If the pressure is not reduced, eventually muscles and nerves within the compartment are compromised, causing numbness and tingling in the feet. In severe cases, muscle death may occur, leading to permanent damage.
Fasciotomy is the splitting of the tight layer of fascia surrounding each of the involved compartments. This allows the muscles to swell during exercise allowing free flow in the blood vessels.
It usually consists of releasing either the anterior, lateral and posterior compartment or all three at the same time.
Antero-lateral release. Longitudinal incisions of about 5 cms each are made over the upper and lower aspect of the leg. The skin is undermined up and down the leg to expose the fascia of the anterior and lateral compartment. The fascia is then cut and split longitudinally and transversely with the excision of a small piece, allowing the compartment to expand.
Posterior release. A 6 cm incision is made at the mid point of the inner side of the tibia. The fascia is released from the border of the tibia and the superficial muscles freed off the back of the tibia and the deep fascia split longitudinally with a small piece excised.
Risks:
- damage to nerves and vessels
- wound infection
After:
- crutches for two weeks, followed by physiotherapy
Anterior compartment
Lateral compartment
Deep posterior compartment
Superior posterior compartment
Following discharge from hospital please see Dr Wood for your first post operative appointment to have your sutures checked 10 to 12 days after surgery.
To book your first appointment with Dr Wood on a Monday morning at the Mater Clinic please complete and submit the following:
Note Clinic Address:
3 Gillies St, Wollstonecraft 2065
Dr Wood uses absorbable / dissolving sutures in most cases.
On the day after surgery remove all bandages from your legs, leaving the plastic dressings. Apply elastic bandages from below knees to ankles.
The hospital will discharge you with pain relief medication which you may require for 48 to 72 hours. Contact your local doctor for further pain management if pain continues and is not relieved by elevation, rest, ice and Panadol.
After surgery you will require crutches to mobilise.
Contact Dr Wood or your local doctor if you notice increased calf pain. Blood clots are uncommon but can occur following surgery.
Contact Dr Wood or your local doctor if the pain in your legs does not subside, if you have a temperature or if you find that you are sweating at night.
Expect some swelling of feet in the few days following surgery.
Physiotherapy - Dr Wood will advise at the time of your first post operative appointment when you can commence physiotherapy.
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
This operation is done to reduce pain by changing the pressure placed on the damaged joint surface (the arthritic part of the knee) and transferring the pressure to the more normal cartilage and bone of the other less affected side of the knee.
A wedge of bone is cut out below the knee, making the knee “knock-kneed" instead of “bow legged".
A high tibial osteotomy is usually performed for people who have osteoarthritis of the knee joint after many years of wear and tear or an old injury. It is usually performed on younger patients (30 to 60 years) who have osteoarthritis on the inside of their knee. This surgery is preferable to a total knee replacement when the patient is young and intending to return to an active lifestyle.
High tibial osteotomies have a 70% chance of giving good pain relief which means that just under one third of patients do not have the result from surgery they expect. It is therefore necessary to be very sure of the risks of surgery to make an informed decision before proceeding.
Surgery is performed at the Mater Private Hospital and the length of stay is two to three days.
The potential complications of surgery are infection, deep vein thrombosis (blood clots), non union of bone, damage to lateral vessels and nerves and failure of the operation to relieve the patient's symptoms.
The surgery involves taking out a wedge of bone from below the knee and a metal plate and screws are applied to the bone to keep it stable. A drain is inserted and absorbable (dissolving) sutures are used to close the wound. The knee is wrapped in bandages and a brace applied.
The drain will usually be removed the day after surgery. The patient will require a brace and use crutches for six weeks.
The patient will see Dr Wood two weeks after discharge to check the wound and be given a referral to a physiotherapist to begin physiotherapy of the knee.
The patient should be able to return to work after three months (depending on the type of work the patient does). It takes six months to fully recover.
On discharge you will be wearing a brace for six weeks. Weight bearing should be with crutches, allowing only partial weight through your operated leg.
Please make an appointment to see Dr Wood to have your wound checked 10-14 days after surgery on a Monday morning at The Mater Clinic.
To book your appointment with Dr Wood at the Mater Clinic please complete and submit the following:
Note Clinic Address:
3 Gillies St, Wollstonecraft 2065
Dr Wood uses absorbable sutures in most cases.
This is your first post operative visit with Dr Wood, and physiotherapy of the knee may commence at this stage.
The next post operative appointment is six weeks after surgery, at which time an x-ray will be required to assess the healing of the osteotomy. The brace will be removed and weight bearing can be increased as tolerated.
Return to work is highly variable and dependent on your occupation.
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
A patellofemoral reconstruction or re-alignment is performed to correct recurrent instability, dislocation or “giving way" of the knee.
The patella or knee cap slides up and down a shallow groove (the trochlear groove) and is kept on track by ligaments and muscles. Mal-tracking, instability or giving way occur when the ligaments and muscles are either weak, too tight, torn, stretched, etc. Sometimes the patella pops in and out of the groove during motion, which is known as subluxation.
Patients are hospitalised for one to two nights and discharged on crutches (usually required for six weeks) and braced for approx. six weeks. The wound should be kept dry for ten to fourteen days when the patient should see Dr Wood for a check up consultation. A second consultation is required at six to eight weeks with an x-ray to check tibial tubercle union.
Sedentary or office workers usually return to work two to four weeks after surgery. Labourers usually require twelve weeks off work.
Infection, deep vein thrombosis or blood clots, numbness on the skin, recurrence
0 – 6 WEEKS
Usually locked at 0°. Brace and static quadriceps rehabilitation
Short VMO re-training. Touch weight bearing only.
6 - 8 WEEKS
Full weight bearing and static quadriceps
Work range to limit. Continue with VMO work
8 - 10 WEEKS
Active quadriceps rehabilitation and increase range of motion to 90°
10 - 12 WEEKS
Go for full range of motion and full active quadriceps
12 - 14 WEEKS
Mini trampoline, bike riding, etc.
After 14 weeks
Full activities if quadriceps fully rehabilitated.
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Proximal hamstring tendon avulsion is a rare and often difficult injury to treat. Depending on the type of avulsion you may experience immediate disabling pain and weakness, extensive bruising, swelling, an inability to run or walk and/or discomfort or pain with prolonged sitting.
There are five types of avulsions:
Type IBone avulsion
This occurs when a portion of the ischial tuberosity (commonly called the bottom or sitting bone) breaks off with the tendon attached.
Type 2Musculotendinous
This occurs when the avulsion (tearing away) occurs between the hamstring muscle and the tendon.
Type 3Incomplete
An incomplete avulsion is when part of the tendon has torn away, but part remains attached to the ischial tuberosity.
Type 4Complete (no retraction)
A complete avulsion with no retraction occurs when the tendon has completely torn away from the ischial tuberosity but has not “coiled up" or descended further down the leg.
Type 5Complete (with retraction)
A complete avulsion with retraction occurs when the tendon has completely torn away and has “coiled up" or retracted to somewhere lower down the leg. (Type 5 avulsions more commonly involve post operative bracing).
Surgery will involve inserting two or three “anchors" in the ischial tuberosity with sutures fixed to them. The sutures are passed through the tendon ends and the tendon is snugly re-approximated to the ischial tuberosity.
The sciatic nerve sits very close to the hamstring tendon and scarring of the nerve may occur if the injury is left indefinitely. For this reason, Dr Wood will perform a “neurolysis" as part of the surgery. This involves identifying the sciatic nerve and carefully releasing any adhesions or scar tissue.
You will be hospitalised and discharged on crutches (usually required for at least two weeks). Bracing (approx. 6 weeks) is occasionally necessary in chronic ruptures. Crutches need to be taken to the hospital.
To perform the surgery, Dr Wood will make a 5-7 cm incision extending from the top of the thigh to the start of the buttock. After surgery, the wound will be covered with a waterproof bandage. You may shower but keep the bandage dry. You will be unable to sit on the wound for at least four to six weeks. A small foam block cushion is helpful to prop up your uninjured side to lessen pressure on the wound. Bar stools are also good because you can sit your good side on the edge of the stool and let your wounded side hang off. You will have to “hover" using your arms for support when going to the toilet.
You should be partial weight bearing for the first several days. Use your crutches and allow your leg to rest. After several days you will be able to put light pressure on your leg but do not be tempted to overdo it. Using crutches for the first two weeks will allow the surgical site to heal more effectively. When you see Dr Wood two weeks post surgery he will advise when it is safe to cease using crutches. If you are braced you will require crutches until the brace is removed.
The hospital physiotherapist will show you a simple non weight bearing range of motion exercise for your leg. Do not attempt anything more than that for the first two weeks.
You will have post operative check ups with Dr Wood at approximately two weeks, six weeks, twelve weeks and twenty four weeks. The recovery process is gradual and Dr Wood may recommend physiotherapy between six and eight weeks after surgery. Do not have physiotherapy or attempt exercise without Dr Wood's clearance.
Initially your leg will feel swollen and bruised and can also feel a bit tingly and numb around the wound site. Whilst the bruising will resolve fairly quickly, it is normal for swelling to come and go (dependent on your activity level) and the tingling/numb feeling to persist for several months. This is due to the many nerves affected by the surgery and should resolve over time. Ice is an excellent anti inflammatory and anti inflammatory medications can be taken for swelling and discomfort.
Once you start moving around a bit more it is important not to overdo the use of your leg. Swelling and discomfort will indicate that you have done too much. Avoid situations that might cause you to fall, change direction quickly or take long strides, spend a lot of time on your feet, etc. You cannot expect to regain full function for up to six months, although you will be moving freely before then. Remember that it may look fine on the outside but you have undergone a major surgical procedure and patience is required to ensure optimal internal healing.
Potential complications include infection, blood clots, damage to the sciatic nerve and an inability to re-attach the hamstring.
You should be able to drive at six weeks post operatively.
Following discharge from hospital please see Dr Wood to have your sutures checked 10 to 12 days after surgery on a Monday morning at the Mater Clinic. This will be your first post operative appointment with Dr Wood. Please complete the following and submit to make your appointment:
Please note address of the clinic:
3 Gillies St, Wollstonecraft 2065.
Dr Wood uses absorbable/dissolving sutures in most cases.
Your wound should be kept dry until the appointment. You will be sent home with a water resistant dressing on your wound which can be replaced if necessary.
The hospital will discharge you with pain relief medication which you may require for 48 to 72 hours. If the pain continues and is not relieved by rest and Panadol you should contact your local doctor for pain management.
When mobilising use crutches and partial weight bear until review at your first appointment. If a brace has been applied do not remove or alter the settings.
Contact Dr Wood or your local doctor if you notice increased calf pain. Blood clots are uncommon but may occur following surgery.
Contact Dr Wood or your local doctor if the pain increases, if you have a temperature or if you find that you are sweating at night.
Expect some numbness down the back of your thigh.
If you develop any weakness in your foot movements contact Dr Wood immediately.
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
Arthritis of the knee joint (usually osteoarthritis) is basically wear and tear of the joint. The knee can wear out because of age or because of a previous injury which accelerates wearing of the knee joint.
Pain may have been experienced in one or both knees for some time, with limited movement when squatting or walking up and down stairs. There may also be a “crunching" of the knee which can be heard and felt when bending the knee.
On examination of the knee, Dr Wood may request an X-ray to confirm the diagnosis by viewing the joint space, the gap between the thigh bone (femur) and shin bone (tibia). This gap is usually made up of meniscus and articular cartilage (similar to the shiny white gristle seen on the joint. Articular cartilage does not show up on X-ray and thus appears as a gap.
If this articular cartilage is worn out by a previous injury or by wear and tear, the gap or joint space narrows, sometimes to the degree where bone rubs on bone and becomes very painful, causing crunching of the knee.
The options for treating arthritis depend on a number of factors:
These factors also help Dr Wood decide on the treatment of the arthritic knee - conservative treatment or surgery.
Conservative treatment is usually chosen for younger people (30 to 60 years) when the disease is mild to moderate and little pain is experienced. This may include anti inflammatories, physiotherapy and a change in lifestyle ie avoiding all twisting sports or change of job. Some people can go on for many years being treated conservatively and some deteriorate rapidly to severe pain which may require surgery.
Surgery may be recommended for older patients who have severe pain and arthritic changes on X-ray.
For those people who are still young (40 to 60 years) a high tibial osteotomy may be necessary to alleviate the pain and grinding of the joint. This operation is 70% successful and thorough discussion with Dr Wood is necessary before proceeding to surgery.
A successful high tibial osteotomy is especially good for those people who wish to return to an active lifestyle with little restriction on activities.
For the more senior patients (60+ years) a total knee replacement may be necessary when pain in their knee is constant and prevents them from enjoying a good quality of life eg walking to the shops or playing nine holes of golf. If a patient has pain at rest and at night preventing sleep it is probably time for a total knee replacement.
It is important to emphasise that a total knee replacement is only performed to relieve pain. It will not enable you to kneel, play netball, touch football, ballet or any twisting type activities or sports. It will help improve the quality of life so that you can walk to the shops or play golf.
Sometimes a knee replacement will be performed on a younger person (40+ years) if their arthritic knee pain is severe and their quality of life is poor.
This operation is 95% successful but with a recovery time of six months. Thorough discussion with Dr Wood involving the potential complications of this operation is necessary. Only when you are prepared to accept the risks of surgery should you consider having this performed.
The chances of developing post traumatic arthritis is not because of the surgery but because of the injuries. The chance of arthritis is 100% after about 7 – 10 years, if the medial meniscus tore. The chance of arthritis is 100% after about 4 – 5 years, if the lateral meniscus tore.
How bad the arthritis will be depends upon the patient's body physiology and the other damage done to the knee at the time of the injury when the meniscus tore. However, if the torn meniscus is allowed to remain in the knee the amount of arthritis will usually be greater, more painful, and will develop much faster than if the torn part of the meniscus is removed.
The time has come, possibly after many years of pain and discomfort, to replace your worn knee joint.
It is important to understand a few things concerning your knee. The operation is performed for one reason only – pain relief. Afterwards you will not be able to kneel, squat, crawl, climb ladders, play tennis, jog or do any other twisting type sports. It will help you walk eighteen holes of golf without pain, or walk to your local shops.
Recovery from your operation will take some time – five to seven days in hospital for a single joint replacement and then recuperation for a further week in a rehabilitation hospital. This depends on your post operative recovery and your situation at home - if you have someone who can help look after you.
No two knees are the same and everyone recovers at a different rate for a number of different reasons (eg fitness, other affected joints and medical problems). If both knees are operated on then one will recover more quickly than the other.
How does the knee work?
The knee joint functions like a hinge at the junction of two bones, the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone). The ends of the bones are covered with a thick cushion of hard white cartilage. There is only one coating of this cartilage in a lifetime and if it is damaged or worn away, the underlying bones rub together, producing the pain and inflammation typical of arthritis.
What is arthritis?
Arthritis is inflammation of a joint causing pain, swelling, stiffness, instability and often deformity. Severe arthritis interferes with activities and limits lifestyle.
What causes arthritis in the knee?
Osteoarthritis or Degenerative Joint Disease. The most common type of arthritis. Osteoarthritis is also known as “wear and tear arthritis" since the cartilage simply wears out. When cartilage wears away, bone rubs on bone causing severe pain and disability. The most frequent reason for osteoarthritis is genetic, since the durability of each individual's cartilage is based on genetics.
Trauma can also lead to osteoarthritis. A bad fall or blow to the knee can injure the joint. If the injury does not heal properly, extra force may be placed on the joint, which over time can cause the cartilage to wear away.
Inflammatory Arthritis. Swelling and heat (inflammation) of the joint lining causes a release of enzymes which soften and eventually destroy the cartilage. Rheumatoid arthritis, Lupus and psoriatic arthritis are examples.
How can a doctor diagnose arthritis?
Doctors diagnose arthritis with a medical history, physical examination and X-rays of the knee.
What is a total knee replacement?
When the cartilage has worn away, an artificial knee (called a prosthesis) can take its place. The surgery to implant the prosthesis is termed a total knee replacement. Only the surface of the joint is removed. The arthritic ends of the bones are shaved off and replaced with new metal and plastic surfaces. The knee replacement recreates some, but not all, knee functions.
Who should have a total knee replacement?
The most common reason for a total knee replacement is severe arthritic pain. Pain cannot be measured, and the degree of pain sufficient to warrant surgery should be decided by the patient and doctor together. Painful and arthritic knees often become unstable and untrustworthy, causing falls and other injuries. The patient's independence is compromised and the quality of their life will decrease.
What are the benefits of total knee replacement?
The goal of a total knee replacement is to relieve pain. It may also help to restore motion and straighten the limb.
What is the short term outlook?
Most patients can stand the second day after surgery and begin exercising that day. With the support of walkers or crutches, patients can walk with confidence, climb stairs and ride in a car by the time they leave hospital. Physiotherapy and motion exercises help recovery and should continue for months. Some swelling, aching and numbing are normal during this time. Most patients are up and about within six weeks.
Surgery
Surgery will be performed at the Mater Private Hospital on a Monday afternoon. Hospital staff will admit and prepare you for surgery. The Anaesthetist will see you prior to surgery. Please advise the Anaesthetist of any medications you are taking.
There are two parts to the surgery:
Firstly: the femur is cut and a titanium femoral prosthesis is put in place.
Secondly: the tibia is cut and a titanium tibial plate is put in place with four screws. A plastic articulating cartilage is placed inbetween the femur and tibia to act as a shock absorber, as well as a barrier between the metal. If the plastic wears out it is easily replaced.
In some knees the patella (knee cap) will also be resurfaced.
A drain will be in place for a couple of days and the wound closed with dissolving sutures or skin clips. Your leg will be wrapped with cotton wool and crepe bandages.
If you had an epidural anaesthetic in your back this will help with pain relief post operatively. If not, recovery and ward staff will offer pain killers.
You will commence physiotherapy (usually the day following surgery) to help you mobilise as soon as possible.
Risks of surgery:
The anaesthetic can cause problems. Discuss any concerns with your Anaesthetist.
Blood clots (DVTs) can form following surgery. You will be given blood thinners in hospital and checked about the seventh day for blood clots with an ultrasound machine.
Infection is the most difficult problem to treat and occurs in about 1% of patients. You will be given antibiotics in hospital.
If you take Aspirin or Warfarin please advise your doctor as you will cease taking it about ten days prior to surgery.
Post operatively
Your recovery depends on you. Remember to take it easy and not overdo things during your immediate post operative period.
The healing process for a total knee replacement can be very slow. It can take up to six months to fully recover – depending on your circumstances it may be more or less than this time.
It is important not to compare yourself with others who have had this surgery as each individual's recovery is different.
Knee replacements are painful for at least three months and some longer. You will never get full bend back or normal function.
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
This app requires Google Chrome to continue. Tap the icon, copy link, then paste into Chrome
This app requires Google Chrome to continue. Tap the icon, Open in browser, then choose Chrome
Dr Wood
| App category: | Healthcare & Medical |
| Updated: | April 2, 2016 |
| App Publisher: | Dr Wood |
| Compatible with: | iOS 6+, Android 4+, Blackberry 10+ and Windows Phone 8+. |
| Legals: | Terms of use |
You successfully shared the app
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?
You successfully shared the app
https://drwood.shareableapps.com/
Tap and hold link above to copy to clipboard.
Are you sure you want to delete this message?